Math can feel like a foreign language sometimes, right? With all those symbols, squiggles, and signs, it’s no wonder many learners get overwhelmed. But here’s the thing—mathematical symbols are just shortcuts to express ideas clearly and quickly. Whether you’re brushing up on basic arithmetic or stepping into advanced mathematics, this guide breaks it all down. Let’s walk through the common math symbols—from everyday basic operations to the more abstract concepts—so you can read mathematical equations with confidence.
Math Symbols Made Simple: A Friendly Guide for All Learners
These are the symbols you’ll run into from your very first math lesson. They form the core of basic arithmetic and show up everywhere—from price tags to baking recipes.
Addition (+)
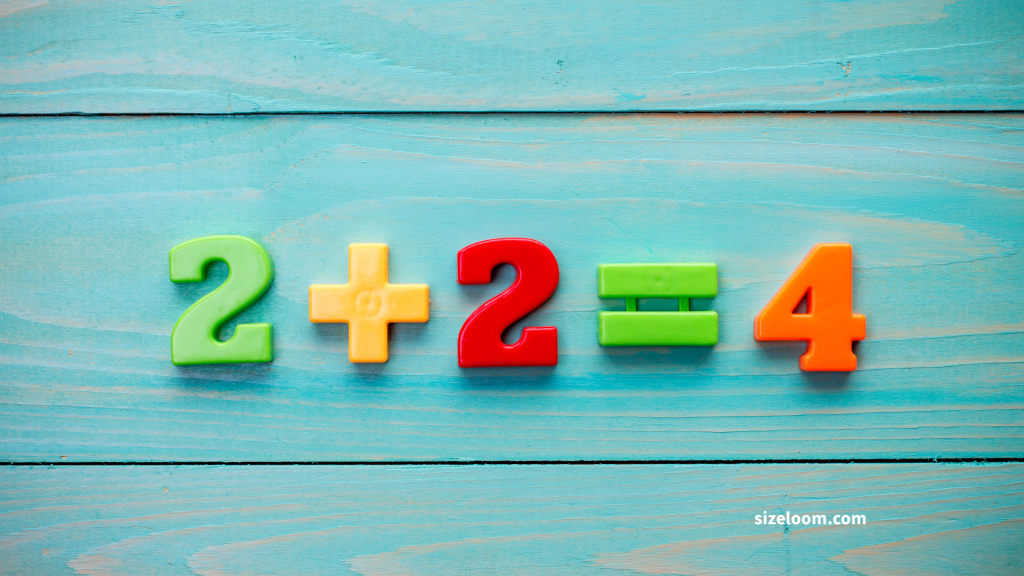
The addition symbol tells you to combine numbers. It’s that simple.
Example: 3 + 2 = 5 Think of it like adding apples in a basket—3 red, 2 green, all together make 5. This essential operation is often your first intro to mathematical concepts.
Don’t Miss: 10 Familiar Objects with a 3-Inch Length (With Images)
Subtraction (-)

Subtraction is the symbol for taking something away.
Example: 7 – 4 = 3 Got 7 candies, give 4 to a friend—you’re left with 3.
It’s used often in basic equations and everyday practical applications like budgeting or time calculation.
Multiplication (× or *)

Here’s where it gets interesting. Multiplication is repeated addition.
Example: 4 × 3 = 12 (or 4 * 3 = 12 in most digital formats) Instead of 4 + 4 + 4, you just write 4 × 3. In coding or spreadsheets, the asterisk (*) is the go-to formal multiplication symbol.
Division (÷ or /)
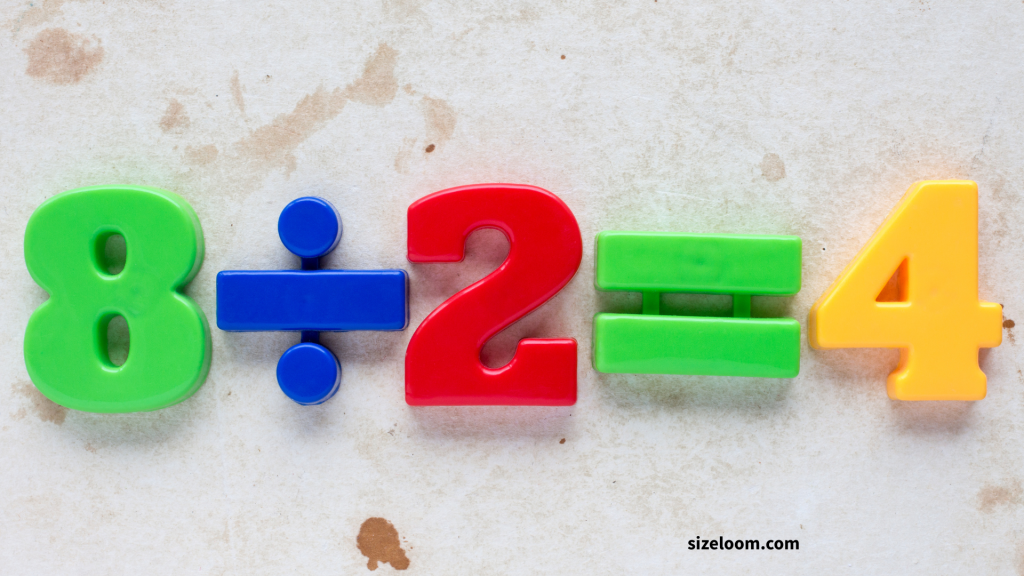
The division symbol shows how to split things equally.
Example: 12 ÷ 4 = 3 (or 12 / 4 = 3)
This symbol is key in cooking (cutting recipes), splitting bills, and understanding fractional quantities. You might hear it referred to as the division sign or division symbol, especially in worksheets.
Equality (=)

The equals sign means the values on both sides are the same.
Example: 5 + 2 = 7
It’s the foundation of all mathematical equations. If you’ve ever heard someone say “It doesn’t add up,” this is what they’re talking about.
Inequality Symbols (<, >, ≤, ≥)
These symbols show relationships between numbers that aren’t equal.
- < means less than
- > means greater than
- ≤ means less than or equal to
- ≥ means greater than or equal to
Used in comparing prices, measurements, or even grades.
Exponentiation (^)
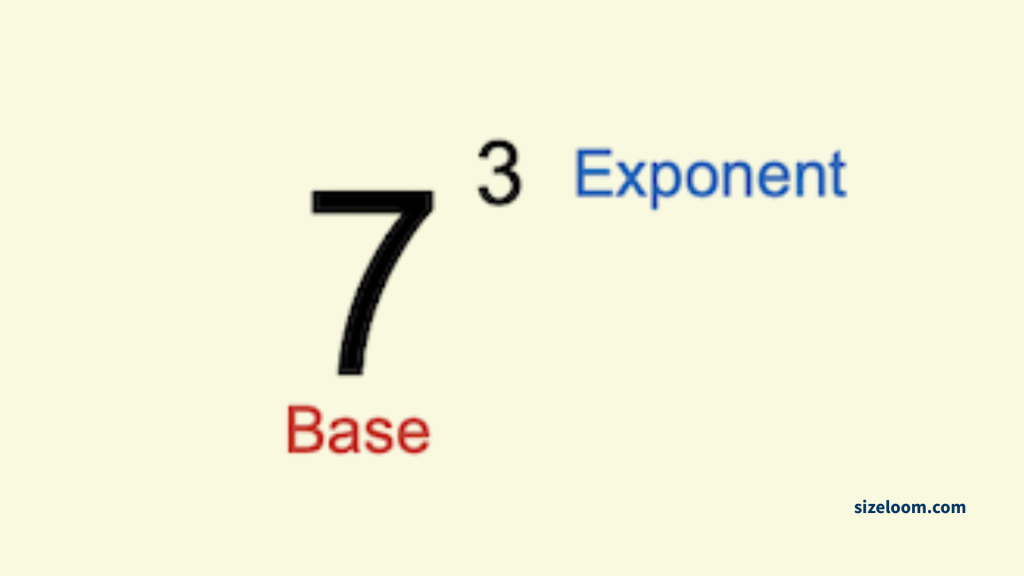
The caret (^) shows that a number is raised to a power.
Example: 2^3 = 8 (which means 2 × 2 × 2)
This exponentiation symbol pops up often in algebraic symbols and quadratic equations.
Square Root (√)

The square root symbol (√) finds a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
Example: √9 = 3 because 3 × 3 = 9
It’s a classic in geometry and one of the most fundamental symbols in math.
Pi (π)

Ah, π—the never-ending number. It’s used to calculate things related to circles.
Example: Circumference = 2πr (Where r is the radius)
It’s a true star in complex math concepts and has its own fan club (yes, really—there’s even a Pi Day!).
Sigma (Σ)

This Greek letter is used to represent a sum of multiple terms.
Example: Σ (i=1 to 5) i = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
A key player in statistics, linear algebra, and vector spaces.
Integral (∫)
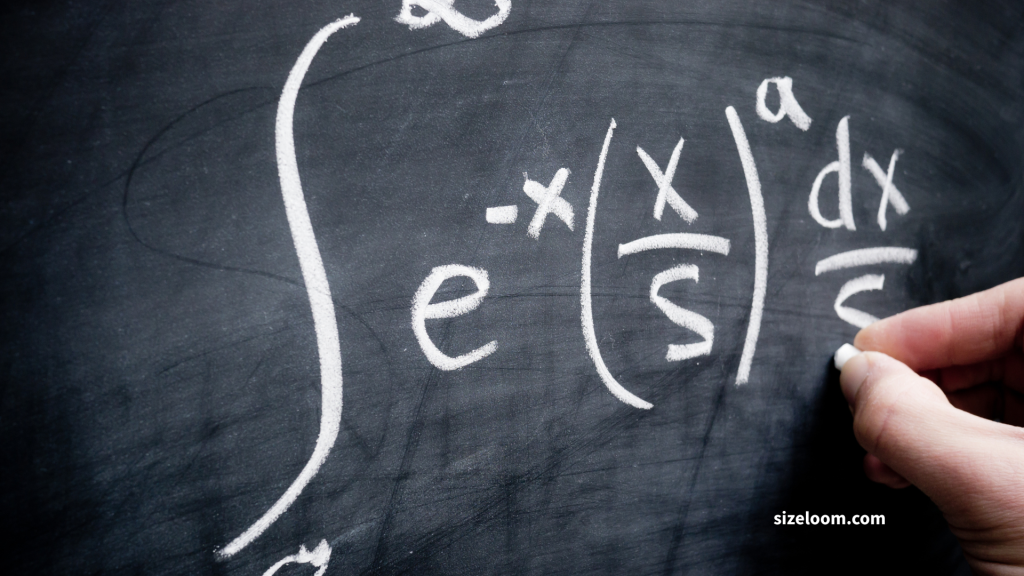
The integral symbol (∫) comes from calculus and represents continuous summing. It shows up when calculating areas under curves—so you’ll see it a lot in advanced calculus and differential equations.
Check this Out: 13 Things That Stretch Around 3 Kilometers Long
Advanced Math Symbols
Once you’re past the basics, you’ll encounter symbols that deal with more complex theories and abstract quantities. Here’s a peek at the next level.
Delta (Δ)

The delta symbol (Δ) shows change or difference, often in values.
Example: Δx means “change in x”
It’s crucial in discrete mathematics, physics, and anything involving rate of change.
Infinity (∞)

This infinity symbol represents a value without end.
You’ll see it in topics like limits, or when something goes on forever (like decimals in 1/3 = 0.333…). Used in many branches of mathematics, it’s a philosophical and mathematical idea rolled into one.
Factorial (!)

The factorial symbol multiplies a number by every positive whole number before it.
Example: 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
It’s a wild ride through combinatorics and an essential counting operation in statistics.
Absolute Value (| |)

These bars show how far a number is from zero, ignoring direction.
Example: |-4| = 4 This absolute value symbol is used in measuring distance, often in vector spaces or complex expressions.
Final Thoughts
Sure, symbols in mathematics might look like ancient hieroglyphics at first. But once you see them as part of a universal language, they stop being so scary. Each one—from the humble plus sign to the swirling infinity—represents fundamental concepts used in everything from calculating discounts (hello, percent symbol) to navigating complex equations. Whether you’re revisiting the multiplication table, exploring abstract algebra, or just curious about how complex symbols fit into real-world applications, remember: these signs aren’t just ink on paper—they’re tools for thinking. So next time you see a funny little squiggle in a math book, don’t panic. Say hi, give it a glance, and think of this guide. You’ve got this. Find Your Fit Fast with SizeLoom, Your Sizing Best Friend.


